Neuronavigation-guided surgery is an innovative tool that allows us to perform complex procedures in the brain with unprecedented precision, providing patients with greater safety and better treatment outcomes.
Neuronavigation uses detailed images of the brain, obtained through scans such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT), to create a three-dimensional ‘map’ of the patient’s brain. This map allows us to plan the surgery with millimetric precision.
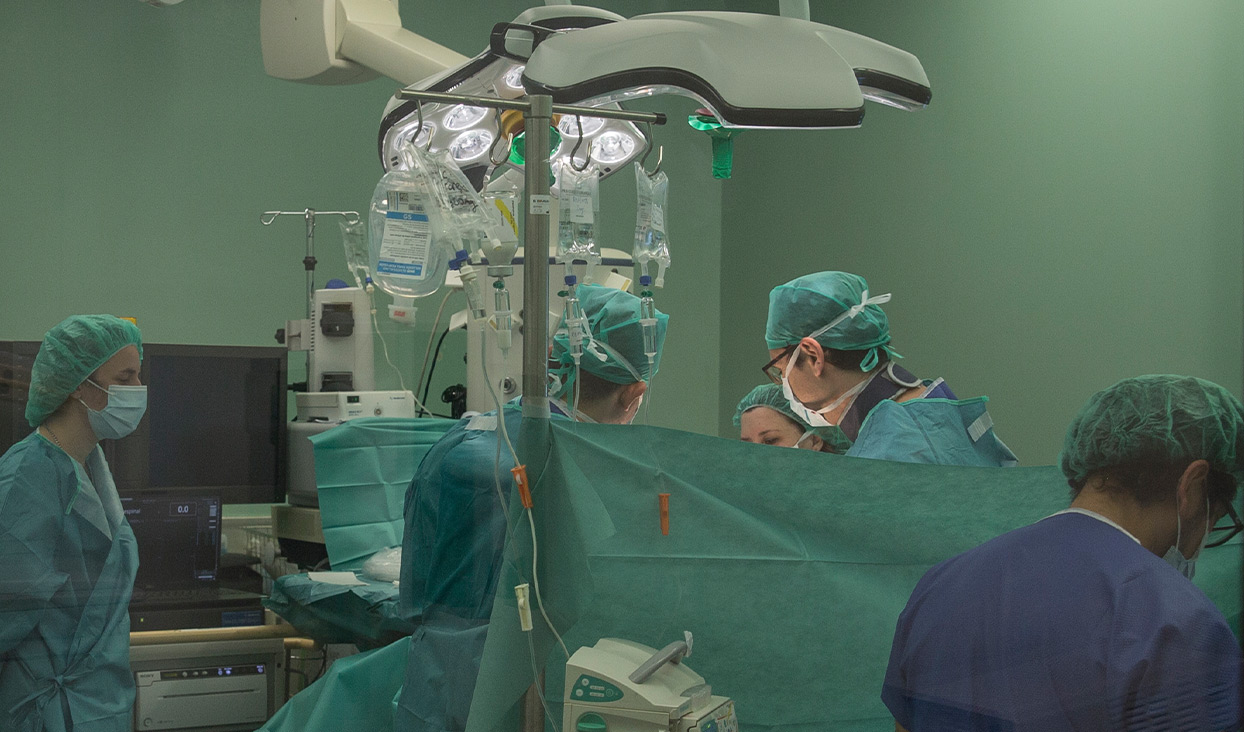
Neuronavigation-guided surgery provides major benefits for the patient, including faster recovery, less damage to surrounding tissues and a reduced risk of complications.
Brain tumours.
Neuronavigation-guided surgery is particularly suitable for treating brain tumours due to its ability to provide exceptional precision during the surgical procedure. By using detailed images of the patient’s brain and real-time navigation technology, we can plan and execute surgery more precisely, helping to reduce the risk of damaging critical areas of the brain that control important functions such as movement, vision or speech. This means that tumours can be removed more effectively and safely, leading to better patient outcomes, including faster recovery.

© NEUROCLÍNICA QUIRÚRGICA BARCELONA 2026 | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | DESIGNED BY VILAX